Virtual Reality (VR) is a digital phenomenon that has intrigued tech enthusiasts and general users alike. But what is VR, exactly? And how does it function? This article aims to dissect these questions and provide a comprehensive understanding of VR, its mechanics, and its real-world applications.
Understanding Virtual Reality
Virtual Reality, often abbreviated as VR, is a technological marvel that employs computer software and hardware to generate a three-dimensional (3D) simulated environment. This digital environment supersedes the real world, immersing the user in a realm of virtual interaction and experience.
Immersion in VR
The key to VR’s appeal lies in its ability to offer immersive experiences. VR doesn’t just present a panorama of images to the user; it promotes an interactive environment where users can interact with others and with the digital world itself. This is accomplished through advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), motion sensors, and tracking algorithms.
The Evolution of VR
The concept of VR has evolved significantly over the years. From being a novel idea in sci-fi literature to becoming a fundamental tool in various industries, VR has undergone a complete transformation.
A Look into the Past
The journey of VR started in the mid-1990s with the advent of the first VR headsets. These devices offered an essential VR experience, primarily influencing the user’s visual perception. As technology advanced, VR headsets became more sophisticated, and new technologies emerged, enhancing the VR experience.
Different Types of VR Experiences
As VR technology matured, it diversified into different experiences, each with unique features and benefits.
Non-Immersive VR
Non-immersive VR provides a basic level of interaction with a digital environment and advanced features like spatial computing or gesture controls.
An example of this is a driving simulator, where interaction is limited to basic controls.
Semi-Immersive VR
Often referred to as “mixed reality,” semi-immersive VR integrates digital elements into natural environments.
This type of VR is commonly used in educational and entertainment settings.
Fully Immersive VR
Fully immersive VR offers a 360-degree simulated experience, replacing the user’s real-world environment with a digital one.
These VR systems use AI and sensors to respond to user actions, creating an interactive virtual world.
Key Components of VR
The VR experience relies on a combination of hardware and software components. These include VR headsets, lenses, screens, spatial audio, and controllers.
- VR Headsets
VR headsets are wearable devices that replace the user’s natural field of view with a computer-generated alternative. The headsets employ screens, cameras, motion sensors, and infrared LEDs to collect and present information to the human eye.
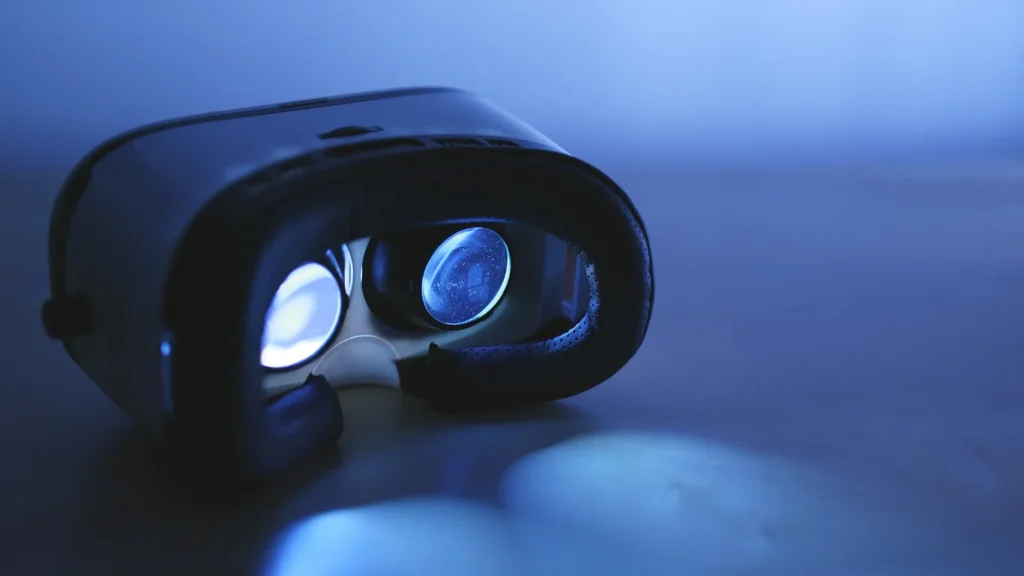

- Lenses and Screens
The VR headsets contain stereoscopic lenses positioned between a screen and the user’s eyes. These lenses distort images to create a three-dimensional effect.
- Spatial Audio
Spatial audio plays a major role in enhancing the VR experience. It positions sound around the user, adding to the realism of the virtual environment.
- VR Controllers
VR controllers are hardware components that enable users to interact with the virtual environment. They allow users to transmit their desired actions directly to the VR software.
- VR Software
VR software integrates various elements of a VR system to produce a 3D virtual world. This software can adapt to various needs, offering industry-specific user experiences.
The Importance of Field of Vision (FOV) in VR
The FOV in VR is crucial for creating a realistic and immersive experience. An ideal VR system should match the natural FOV of the human eye, which is about 120 degrees vertically and nearly 360 degrees horizontally.
Considering Aberrations in VR Design
Like any optical system, VR devices are prone to aberrations, such as axial chromatic aberration, spherical aberration, coma, astigmatism, and field curvature. These aberrations can introduce blur and warping, affecting image quality. Therefore, aberration control is vital in VR optical design.

Advances in VR design incorporate technologies like aspheric surfaces, diffractive optical elements (DOEs), holographic optical elements (HOEs), tunable lenses, and plastic optics. These technologies aid in enhancing VR’s eye-box size and FOV while maintaining a compact form factor.
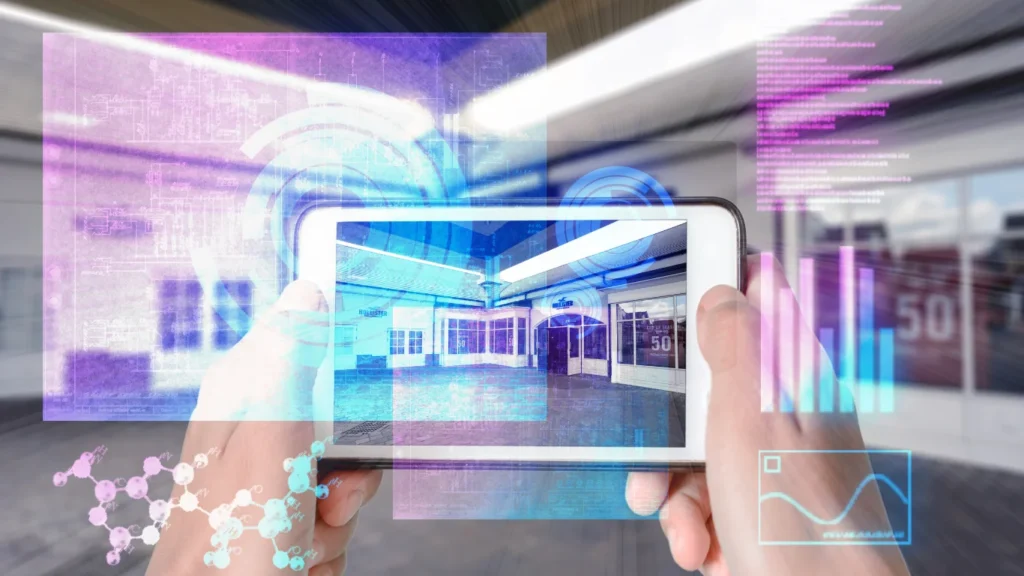
Difference Between VR and Augmented Reality (AR)
While VR completely replaces the user’s real-world view with a simulated environment, AR enhances the real-world view by overlaying digital elements onto it. AR requires high luminance displays, especially for bright environments, and follows a folded design to enable a wide FOV and compact form factor.
Real-World Applications of VR
VR has found applications in various sectors, including education, engineering, social commerce, entertainment, and healthcare. From military training and remote learning to 3D design and virtual interactions, VR is revolutionizing how we interact with the digital world.
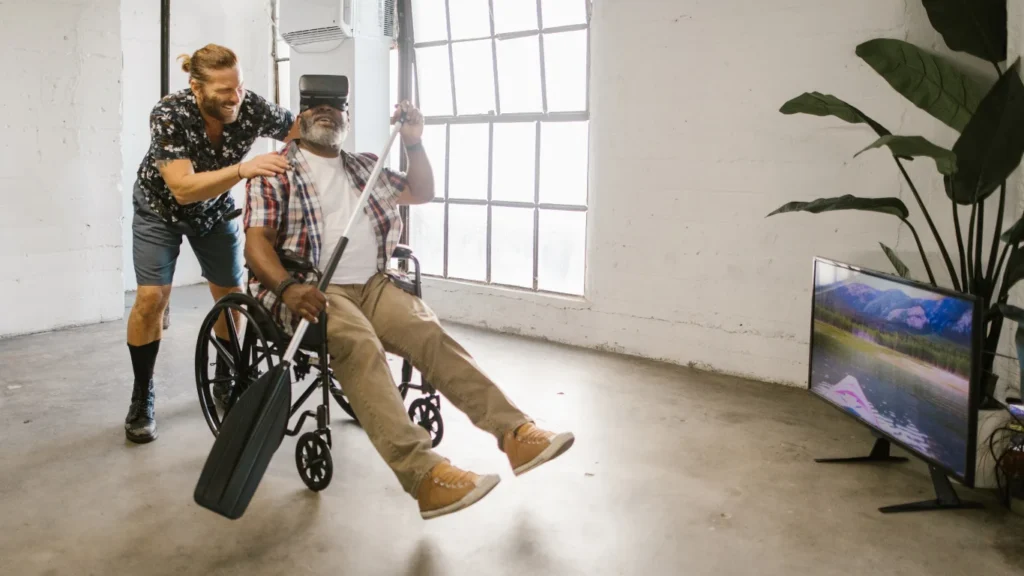

Despite its vast potential, VR faces several challenges. These include issues related to VR sickness, high production costs, environmental impacts due to high computing requirements, and potential ethical and cybersecurity concerns.
The Future of VR
By 2030, the VR market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 27.5%. As technology advances, the VR landscape will continue to evolve, providing more immersive and interactive experiences.
FAQs
Can VR cause health issues?
While VR offers immersive experiences, prolonged exposure can cause VR sickness, leading to headaches and nausea. However, advancements in technology are being made to mitigate these effects.
Is VR used only in gaming?
No, VR has applications that extend beyond gaming. It is used in various sectors like education, engineering, healthcare, and social commerce.
Is VR the same as AR?
No, VR and AR are different. While VR replaces the real-world environment with a simulated one, AR enhances the real-world view by overlaying it with digital elements.
Is VR expensive?
The cost of VR equipment varies depending on the type of VR system. Some systems can be expensive, but there are also affordable options available in the market.
What are the prospects of VR?
The future of VR looks promising, with an expected growth rate of 27.5% by 2030. As technology advances, VR is predicted to offer more immersive and interactive experiences.
To conclude, virtual reality is an intriguing technology that has the potential to transform the way we interact with the digital world. With the advancement of VR technology, we can anticipate more captivating and interactive experiences soon. The opportunities for immersive VR experiences are limitless!