Embedded finance is transforming Australia’s business landscape with unprecedented growth potential. According to a 2024 report by Research and Markets, Australia’s embedded finance market is projected to grow at an annual rate of over 28%, reaching AUD 4.55 billion by 2029. This remarkable expansion comes at a critical time, as Australian small businesses regularly cite cash flow as one of their biggest challenges.
What is embedded finance? At its core, it involves integrating financial services directly into non-financial platforms, making these services available precisely when users need them. Consequently, embedded finance solutions address key operational problems for businesses without requiring separate financial applications or processes. The embedded finance ecosystem comprises various platforms and providers collaborating to deliver seamless experiences across payment processing, lending, insurance, and currency exchange. Furthermore, this approach is gaining traction as a major driver of innovation, customer experience and business growth across industries.
This article examines how embedded finance is transforming Australia’s financial landscape, highlighting the key components of successful implementations, various use cases, and the strategic benefits that businesses can derive from adopting these technologies.
Understanding Embedded Finance in the Australian Context
The Australian financial landscape is witnessing a significant shift as embedded finance continues to reshape traditional banking models. This evolution represents more than just technological advancement—it marks a fundamental change in how financial services reach customers.
What is Embedded Finance Compared to Traditional Banking
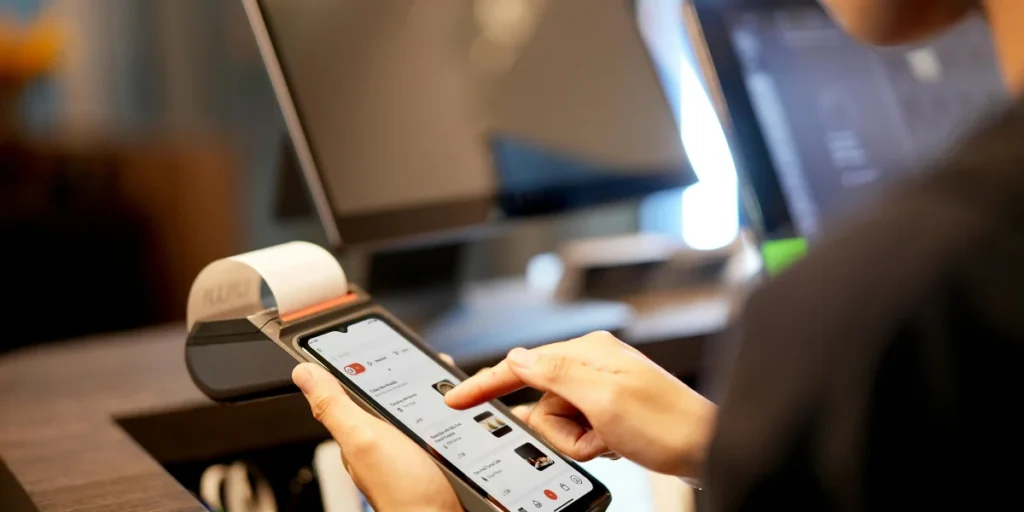

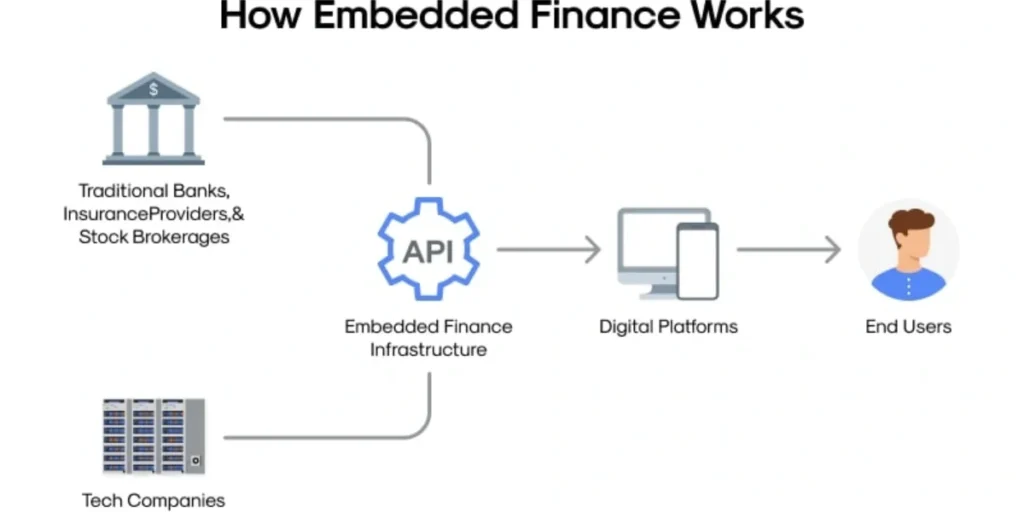
Embedded finance works by offering financial products—such as payments, digital wallets, lending, or insurance—within a non-financial platform. Unlike traditional banking models, where consumers must seek out separate providers for various financial needs, embedded finance brings services directly to customers within their existing digital experience. This integration occurs through APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), which enable different software systems to communicate seamlessly, allowing for smooth data and service flow between businesses and their financial partners.
The key distinction lies in the delivery model. Traditional banks require customers to engage through separate channels, whereas embedded finance places lending at the point of need, enabling instant credit decisions and flexible payment options. Additionally, embedded finance providers supply the necessary licences and infrastructure, allowing non-financial companies to offer banking services without building the underlying systems themselves.
Growing Popularity of Embedded Finance in Australia
Australia has become one of the fastest-adopting regions for embedded finance solutions, driven primarily by fintech innovation, open banking initiatives, and growing consumer demand for seamless digital services. The market is projected to grow at a rate of 9.4% annually, reaching AUD 17.60 billion by 2025, with further expansion to approximately AUD 22.72 billion by 2030.
Several factors fuel this growth. First, Australia’s Consumer Data Right regime enables secure, consent-driven data sharing, allowing providers to tailor products with unprecedented precision. Moreover, the continued rollout of Australia’s New Payments Platform, particularly the PayTo service, is unlocking real-time payment capabilities that were previously impossible. Likewise, sectoral digitisation and increasing collaboration between fintechs and industry-specific platforms are accelerating adoption across diverse industries.
Key Players: Embedded Finance Platforms and Providers
The Australian embedded finance ecosystem features diverse providers serving different market segments. Infrastructure providers like Zepto deliver real-time payment enablement using NPP and PayTo, with solutions embedded in subscription platforms and marketplaces. Similarly, FrankieOne offers onboarding and fraud prevention APIs for compliance-heavy customer acquisition flows.
Other notable players include Monoova, which provides payment automation APIs particularly suited for SMEs and payroll-linked use cases, and Shaype (formerly Hay-as-a-Service), which allows enterprises to embed accounts and card-issuing features. These infrastructure providers create the foundation upon which consumer-facing platforms build their embedded finance offerings.
Core Components of Embedded Finance Solutions
Successful embedded finance implementation relies on four essential technical components that work together to create secure, user-friendly financial experiences. These building blocks form the foundation of any viable embedded finance solution in the Australian market.
API-First Architecture for Seamless Integration
At the core of embedded finance solutions is an API-first approach that prioritises designing and optimising APIs from the beginning of development. This architecture enables different software systems to communicate seamlessly, ensuring financial services remain flexible, scalable, and easy to integrate with other platforms. Specifically, these APIs enable businesses to integrate banking functions directly into their products without building their own infrastructure, thereby significantly reducing integration time.
Modern FinTech cores process thousands of transactions per second through RESTful APIs, webhooks, and standardised data models. This reduces friction for engineering teams building banking features into existing products. Additionally, pre-built modules such as account orchestration, KYC connectors, payout engines, and ledger layers enable businesses to launch new services rapidly – often in weeks rather than months.
Licencing and Compliance: ACL, KYC, AML in Australia
In Australia, embedded finance providers must navigate a complex regulatory landscape. Any entity conducting “banking business” must be licensed as an authorised deposit-taking institution (ADI). Nevertheless, APRA introduced a Restricted ADI framework that permits new businesses to conduct limited banking activities for a period of two years while building their capabilities.
KYC (Know Your Customer) procedures are mandatory, requiring businesses to collect and verify customer information based on the risk levels associated with money laundering and terrorism financing. For individuals, this includes full name and either residential address or date of birth. For companies, verification involves collecting the full name, registration status, and ACN or ARBN. Importantly, businesses must implement risk-based systems to address verification discrepancies, such as mismatched names on identification documents.
User Experience Design for Embedded Financial Tools
Effective user experience design prioritises users’ needs, creating intuitive, relevant, and valuable financial tools. The interface should guide users seamlessly through financial functionalities, making navigation straightforward and tasks easy to complete.
Since financial services involve sensitive information, security elements must be visibly incorporated to build trust. This includes secure padlocks, encryption symbols, and clear privacy policies. Two-factor authentication or biometric verification adds another layer of security protection. Simultaneously, interactive tutorials, informational pop-ups, and tooltips can help users understand complex financial concepts, improving financial literacy.
Real-Time Data Flow and Automation in Embedded Systems
Embedded finance centralises both business and financial operations within applications businesses already use, creating a seamless bridge between financial data and operational platforms. This unified approach can save businesses up to 80% of time previously spent on manual reconciliation, compliance checks, and financial reporting.
Real-time processing ensures transactions and updates happen instantly, eliminating waiting periods. Secure data sharing between the platform, provider, and financial systems maintains integrity throughout the process. Moreover, analytics capabilities enable businesses to learn from user behaviour, fine-tune offerings and suggest better financial products.
Types of Embedded Finance
The embedded finance ecosystem in Australia encompasses a diverse range of financial services tailored to specific business contexts and customer needs. Each type addresses distinct operational challenges while creating new revenue opportunities.
Embedded Payments in E-Commerce and Gig Platforms
Embedded payment solutions enable businesses to process transactions without the need for separate terminals or redirects. Tyro has launched Australia’s first tap-to-pay technology that integrates directly into iOS and Android devices. This technology enables merchants to streamline customer checkout experiences by managing both point-of-sale and payment transactions through a single device. Indeed, 68% of Australian SMBs now seek payment processing services directly from their software platforms.
For gig economy platforms, embedded payments solve critical cash flow challenges. Currently, solutions like digital wallets enable workers to access their earnings instantly after completing tasks—a crucial feature, considering that 60% of gig workers would switch platforms for faster access to earnings.
Buy Now Pay Later and Embedded Credit Options
BNPL services remain the most recognisable form of embedded finance in Australia. These solutions integrate seamlessly into checkout processes, enabling customers to access credit without leaving the shopping experience. Besides traditional retail applications, embedded credit now extends to B2B platforms, offering financing options with instant decisions and flexible terms based on alternative credit scoring methods.
Contextual Insurance and Embedded Protection Plans
Embedded insurance integrates protection directly into purchase journeys, creating friction-free experiences. This sector is projected to reach AUD 53.51 billion by 2033—representing 18% of Australia’s total insurance market. Currently experiencing a 34% compound annual growth rate, embedded insurance significantly outpaces traditional channels, which are growing at a rate of just 4%.
Key implementations include:
- Travel insurance during flight bookings
- Product protection plans for electronics purchases
- Pay-per-mile insurance through vehicle apps
Allianz has pioneered this approach by partnering with carsales.com.au to integrate insurance directly into the online car-buying process.
Multi-Currency Wallets and Embedded FX Solutions
Multi-currency wallets enable businesses to hold funds in various currencies, eliminating conversion costs. Firstly, they allow for collection and settlement in the same currency, thereby eliminating unnecessary exchange fees in cross-border transactions. In fact, embedded cross-border finance infrastructure is projected to reach AUD 351.67 billion by 2025.
Payroll and Lending Integrations for SMEs
Payroll systems are rapidly emerging as critical gateways for embedded finance. These integrations enable access to earned wages before official paydays and facilitate working capital advances during periods of low activity. SME financing embedded within business platforms addresses a substantial AUD 58.10 billion funding gap in Australia, where over half of capital applications face rejection.
Benefits and Strategic Impact for Australian Businesses

Beyond technological innovation, embedded finance delivers measurable business outcomes for Australian companies. Organisations embracing these solutions are discovering powerful strategic advantages throughout their operations.
New Revenue Streams Through Transaction Fees and FX Markups
Australian businesses that implement embedded finance generate additional income through transaction fees, interest earnings, and service charges. Over 70% of surveyed companies believe that more than half of financial services will soon be offered via non-financial platforms. Companies can earn a slice of each payment processed through embedded systems, with some businesses reporting a threefold increase in their customer lifetime value within six months of implementation.
Improved Customer Retention via Seamless Financial Experiences
Embedded finance solutions significantly boost customer loyalty. Companies offering embedded payment options experience 2.5x lower attrition rates compared to those without such integration. Obviously, this retention improvement stems from reduced friction—90% of businesses using embedded finance report increased customer loyalty.
Financial Inclusion for Underserved Business Segments
For SMEs frequently rejected by traditional lenders, embedded finance platforms address a substantial AUD 58.10 billion funding gap. Hence, embedded solutions democratise access to financial features, bringing services to previously underserved populations.
Data-driven Product Development and Personalisation
Perhaps most valuable is the data advantage. Embedded finance generates rich customer insights that drive product innovation and inform strategic decisions. Australia’s Consumer Data Right regime enables unprecedented personalisation, including dynamic credit limits that adjust based on real-time cash flow analysis. Businesses can efficiently turn financial data into new products by using this data-driven strategy to precisely tailor their services to client needs.
Conclusion – Embedded Finance
Embedded finance is at the forefront of Australia’s financial evolution, transforming the way businesses and consumers interact with financial services. Throughout this article, we have seen how this innovative approach integrates seamlessly into existing platforms rather than requiring separate applications or processes.
The Australian market has enthusiastically adopted embedded finance solutions, as evidenced by projections forecasting growth to AUD 22.72 billion by 2030. This rapid adoption primarily stems from the country’s progressive regulatory environment, technological readiness, and consumer demand for seamless experiences.
Beyond merely simplifying transactions, embedded finance addresses critical challenges facing Australian businesses. SMEs particularly benefit from improved cash flow management and access to previously unavailable funding options. Additionally, the data generated through these integrated systems enables unprecedented personalisation and product innovation opportunities.
Looking ahead, embedded finance will undoubtedly continue to reshape Australia’s business landscape. As adoption increases across industries, the distinction between financial and non-financial services will continue to become increasingly blurred. Consequently, companies that strategically implement these solutions now position themselves advantageously for the evolving digital economy. Therefore, Australian companies must consider how these solutions align with their broader strategic goals to remain competitive in an increasingly connected financial ecosystem.
You May Also Be Interested In: 10 Best AI Tools for Small Business: Boost Efficiency & Growth
What is embedded finance, and how does it differ from traditional banking?
Embedded finance integrates financial services directly into non-financial platforms, enabling users to access banking services on demand without the need for separate applications. Unlike traditional banking, which requires customers to engage through dedicated channels, embedded finance seamlessly incorporates financial products into existing digital experiences.
How does embedded finance benefit Australian businesses?
Embedded finance creates new revenue streams through transaction fees and FX markups, improves customer retention by offering seamless financial experiences, promotes financial inclusion for underserved segments, and enables data-driven product development and personalisation.
What are the key components of successful embedded finance implementation?
Successful embedded finance solutions rely on API-first architecture for seamless integration, compliance with Australian licensing and regulatory requirements (including KYC and AML), user-friendly design for financial tools, and real-time data flow and automation capabilities.